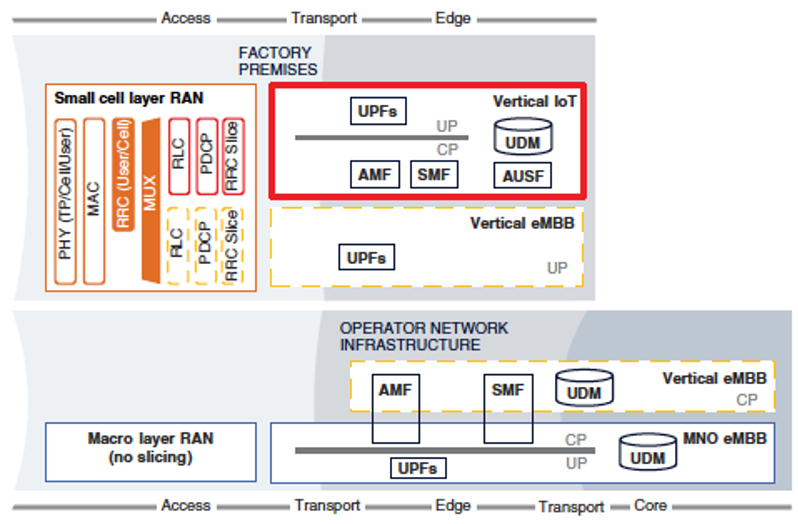
In the intricate tapestry of Industry 4.0, the marriage of private and public network slices in a 5G ecosystem is unlocking unprecedented possibilities for smart manufacturing. Our journey through this landscape has taken us into the heart of a factory scenario where a delicate balance between public Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and enterprise-owned private networks orchestrates a symphony of connectivity. In this continuation, we delve into the nuanced ownership dynamics and deployment intricacies that shape the deployment and operation of distinct network slices tailored for the unique demands of industrial manufacturing.
Ownership Dynamics: Infrastructure, Spectrum, and Subscriber Data
1. Infrastructure and Spectrum:
- The “vertical” emerges as a pivotal player, providing the small cell layer RAN equipment, transport network, and edge cloud resources for all network slices within the factory premises.
- To operate the small cell layer RAN, the vertical rents dedicated spectrum resources from the MNO, strategically confined to the factory premises.
- For eMBB services, both small cell layer RAN and, if required, the MNO-provided macro layer RAN are utilized. The MNO retains control over RRM functions and owns a 5G-compatible network infrastructure, comprising centralized datacenters and distributed edge clouds.
2. Subscriber Data:
- Subscriber information data, including long-term security credentials, is in the possession of the vertical for IoT devices. This ensures full isolation of the vertical’s IoT subscriber information from the MNO.
- For eMBB subscribers, the MNO holds corresponding data for its own eMBB subscribers and vertical eMBB subscribers.
Network Slice Deployment and Operation
1. IoT Network Slice:
- Deployed in a domain-specific manner, all functions reside within the vertical’s domain and are exclusively used by IoT devices registered in the vertical’s home subscriber system (HSS) or Unified Data Management (UDM).
- Local operation of small cell layer RAN, IoT-specific User Plane Processing Functions (UPFs), AMF, and SMF ensures a shielded operation within the factory environment, minimizing exposure to the MNO.
2. Vertical eMBB Slice:
- Deployed in an inter-domain manner, sharing CN control plane functions with the MNO eMBB network slice.
- The MNO retains control over AMF, SMF, AUSF, and UDM for authentication, NAS ciphering, and integrity protection.
- The transport network features independent slices with guaranteed isolation and security for both the vertical and the MNO.
3. Resource Multiplexing:
- PHY and MAC in the UP, and RRC in the CP are shared by both slices in the vertical’s small cell layer RAN, simplifying resource multiplexing and ensuring efficient RAN implementation.
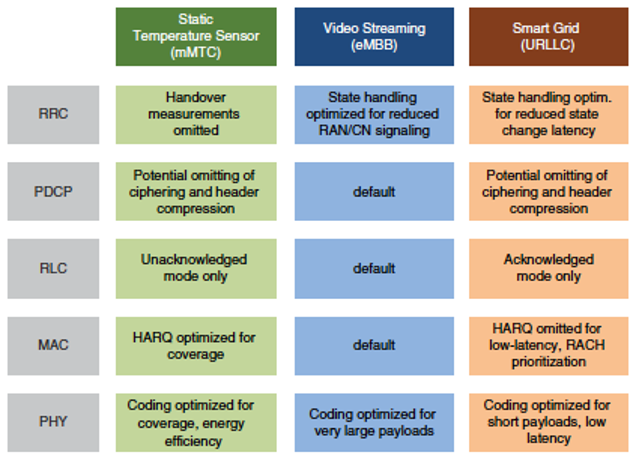
- Customization through configuration and parameterization of RLC, PDCP, and RRC-Slice functions allows each network slice to tailor its operation while maintaining resource efficiency.
Security and Isolation
1. IoT Slice:
- Completely isolated from the operator network, utilizing locally hosted functions and resources. Security termination points and user data remain strictly local, enhancing control and data security.
2. eMBB Slice:
- A “roaming” agreement between the vertical and the MNO assures service continuity for vertical eMBB UEs leaving the factory premises.
- Trust between the MNO and the vertical is essential, with the MNO providing NAS ciphering and integrity protection. Over-the-top security measures can be employed by the vertical to safeguard UP traffic.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Smart Manufacturing
In the evolving landscape of smart manufacturing, the orchestration of private and public network slices through 5G technology not only enhances connectivity but also redefines ownership, security, and deployment paradigms. The delicate dance between the vertical and the MNO sets the stage for a future where Industry 4.0 thrives on the seamless integration of diverse network slices, each finely tuned to meet the unique demands of a connected and intelligent manufacturing ecosystem. As we navigate the complexity, we usher in an era where 5G network slicing becomes the linchpin for the transformative journey toward unparalleled efficiency, innovation, and connectivity. Welcome to the future of smart manufacturing, where the convergence of private and public slices paints a vibrant tapestry of possibilities.

