Introduction:
As we stand on the cusp of the 6G era, the digital transformation of smart building systems is poised to reach unprecedented heights. The requirements for leveraging external cloud solutions in smart homes, buildings, and urban districts/cities applications are evolving, demanding a future-proof network infrastructure to meet the diverse needs of a digitized economy. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the essential requirements that 6G can address to propel the digitization economy of smart building systems.
- High Network Coverage in Residential Areas:
One of the fundamental requirements for the smart building ecosystem is extensive network coverage in residential areas. 6G aims to enhance coverage to ensure that smart devices within homes, buildings, and urban districts seamlessly connect and communicate. The focus is on eliminating connectivity gaps, enabling a robust and reliable network for the myriad of applications that constitute a smart environment.
- High Number of Subscribers:
With the proliferation of smart devices, the demand for network capacity is skyrocketing. 6G is designed to support a high number of subscribers simultaneously, ensuring that the network remains responsive and efficient even in densely populated areas.
- Long-Range, Low-Rate, Low-Power, Low-Cost Managed Services:
6G aims to provide a balance between long-range communication, low data rates, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness. This is crucial for managing smart services efficiently, ensuring that devices can communicate over extended distances while conserving energy and minimizing costs.
- High Transfer Speed for Entertainment Services:
Entertainment services in smart buildings, such as streaming high-quality 4K content, require high transfer speeds. 6G targets a minimum speed of 50 Mbit/s for compressed 4K entertainment services, ensuring a seamless and immersive user experience.
- Fast Handover (< 2ms) and Low Latency (< 2ms):
6G envisions ultra-fast handovers (less than 2ms) to support applications that require rapid mobility, such as autonomous vehicles within smart urban districts. Additionally, low latency (< 2ms) for radio links ensures swift transmission of real-time entertainment services, contributing to an immersive and responsive digital environment.
- High Data Security:
The digitization of smart buildings necessitates robust data security measures. 6G is designed to implement advanced encryption protocols, secure authentication mechanisms, and privacy-preserving technologies to safeguard sensitive information from potential threats.
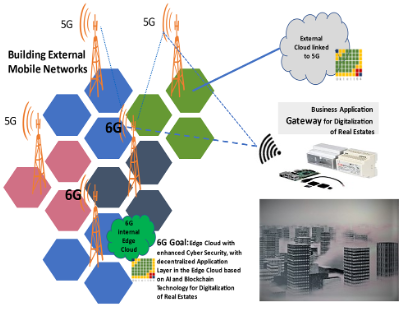
- Deployment of Own 5G/6G Private Network (Campus Network):
Smart building systems often require dedicated, private networks for specific applications. 6G supports the deployment of private networks (campus networks), offering tailored solutions that cater to the unique needs of smart homes, buildings, or urban districts.
- Robust Networks with Less Sensitivity to Interference:
6G addresses the challenges posed by physical barriers such as walls, cellars, halls, high buildings, trees, and adverse weather conditions. The goal is to create robust networks that are less sensitive to interference, ensuring consistent connectivity and performance in diverse environments.
Conclusion:
The advent of 6G promises a transformative leap forward in the digitization economy of smart building systems. By addressing the diverse and demanding requirements outlined above, 6G aims to create a technological ecosystem where connectivity, speed, security, and resilience converge to redefine the possibilities of smart living and urban development. As we look to the future, the vision of 6G holds the key to unlocking the full potential of the digitized smart building landscape.